How to remove TABLESPACE in PostgreSQL
- GeekGuy
- Apr 26, 2022
- 1 min read

In PostgreSQL, the DROP TABLESPACE statement is used to remove a tablespace.
Syntax: DROP TABLESPACE [IF EXISTS] tablespace_name;Let’s analyze the above syntax:
First, specify the name of the tablespace that is to be deleted after the DROP TABLESPACE keywords.
Second, use the IF EXISTS option to handle errors in case the tablespace doesn’t exists.
Note: It is important to note that only tablespace owners or superusers can execute the DROP TABLESPACE statement.
Example:
First, we create a new tablespace named gfg and map it to the C:\data\gfg directory:
CREATE TABLESPACE gfg
LOCATION 'C:\data\gfg';Now create a database named db_gfg and set its tablespace to gfg:
CREATE DATABASE db_gfg
TABLESPACE = gfg;Now create a new table named test in the db_gfg and set it tablespace to gfg:
CREATE TABLE test (
ID serial PRIMARY KEY,
title VARCHAR (255) NOT NULL
) TABLESPACE gfg;The following statement returns all objects in the gfg tablespace:
SELECT
table_space.spcname,
class.relname
FROM
pg_class class
JOIN pg_tablespace table_space
ON class.reltablespace = table_space.oid
WHERE
table_space.spcname = 'gfg';This will lead to the following:
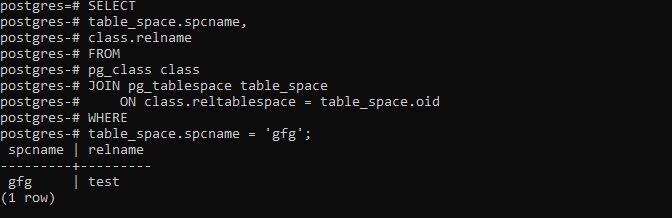
Now if you try to drop the gfgtablespace:
DROP TABLESPACE gfg;This will raise the following error:

As the gfg tablespace is not empty,it is not possible to drop the tablespace. Now, login to the Postgres database and drop the db_gfg database:
DROP DATABASE db_gfg;Now delete the gfg tablespace again:
DROP TABLESPACE gfg;Now check for the tablespace using the below command to verify:
\db+Output:


Commentaires